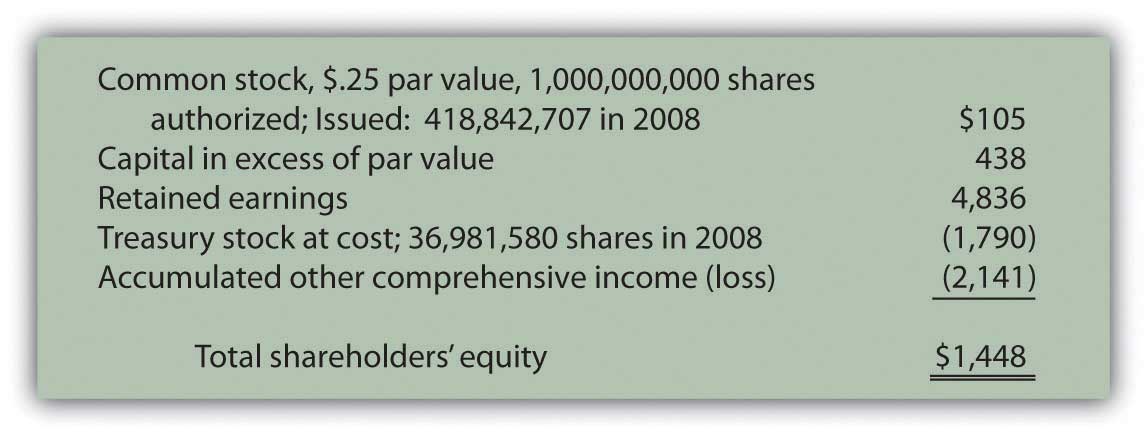
Companies might choose to use a form of balance sheet known as the common size, which shows percentages along with the numerical values. The value of $60.2 billion in shareholders’ equity represents the amount left for stockholders if Apple liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities. Retained earnings are a company’s net income from operations and other business activities retained by the company as additional equity capital. They represent returns on total stockholders’ equity reinvested back into the company. Some investors may have large ownership interests in a given corporation, while other investors own a very small part. To keep track of each investor’s ownership interest, corporations use a unit of measurement referred to as a share (or share of stock).
- The calculation for common stock outstanding can seem a little daunting at first simply because so much accounting jargon is used to define and calculate it.
- In this example, Apple’s total assets of $323.8 billion is segregated towards the top of the report.
- How much of the business your one share buys depends on the total common stock outstanding, a figure you can easily determine using the company’s balance sheet.
- Broadly defined, common stock can be thought of as the bedrock of a company’s public offerings.
- Preferred stock combines features of both stocks and bonds, offering a potentially more stable income stream, with less volatility than common stock.
Advantages of preferred stock
Some prominent examples of companies that offer preferred shares include Bank of America, AT&T, and Wells Fargo. These companies use preferred stock to raise capital without giving voting control to new investors. The additional paid-in-capital for each class of stock has also been presented separately.
How to Invest in Preferred Stock

Common stock in a balance sheet of a company is recorded in the “stockholders’ equity“. This is where investors can calculate the book value, or net worth, of their shares, which is equal to the assets minus the liabilities of the company. Therefore it is essential that financial managers get this recording process xero courses in melbourne right. It offers the chance for price appreciation and usually comes with voting rights, allowing you to have a say in crucial company decisions. Preferred stock, on the other hand, provides a more stable option with regular dividend payments and less credit risk if the company goes into liquidation.
How to Calculate Common Stock on Balance Sheet
The more shares you have, the louder your voice, particularly in voting on the board of directors or on policies affecting the value of the stock. The company may occasionally issue common stock in exchange for services received or rendered. In this situation, it is necessary to give the service a specific value (Monetary value). As an illustration, the XYZ startup agrees to pay the $30,000 in attorney fees through the issuance of equity.
It is calculated either as a firm’s total assets less its total liabilities or alternatively as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares. Stockholders’ equity might include common stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock. When a company issues shares of common stock, it gets money from investors, increasing the common stock balance in its financial records. This money, representing the amount of common stock sold, is recorded as paid-in capital in the equity section.
What is the difference between Common Stock and preferred stock?
Preferred stock is assigned an arbitrary par value (as is common stock, in some cases) that has no bearing on the market value of the shares. The common stock and preferred stock accounts are calculated by multiplying the par value by the number of shares issued. Assume a corporation has been authorized by the state in which it is organized to issue 500,000 shares of common stock with no par value. If the corporation actually issues only 100,000 shares for $50 each, the corporation will debit its Cash account for $5,000,000 and will credit its account Common Stock for $5,000,000. The corporation will now have 100,000 shares of common stock outstanding. If a stockholder owns 1,000 shares of the common stock, the stockholder owns 1% of the corporation.
It shows that the company has more resources because of the investment from common shareholders. As an example, assume a company issues 1,000 common shares with a stated value of $5 per share, and investors purchase all 1,000 shares for $15 per share. The company records common shares for $5,000 (1,000 shares outstanding x $5 stated value per share) in the shareholder’s equity section on their balance sheet.
These earnings, reported as part of the income statement, accumulate and grow larger over time. At some point, accumulated retained earnings may exceed the amount of contributed equity capital and can eventually grow to be the main source of stockholders’ equity. For this reason, many investors view companies with negative shareholder equity as risky or unsafe investments. Shareholder equity alone is not a definitive indicator of a company’s financial health. If used in conjunction with other tools and metrics, the investor can accurately analyze the health of an organization. The certificate would indicate the type of stock (common, preferred), any restrictions pertaining to the sale of the stock, the number of shares, the par value, etc.