Current assets and plant assets represent two distinct types of assets on a company’s balance sheet, each serving different financial and operational roles. In contrast, plant assets are long-term assets like buildings, machinery, and equipment that contribute to the company’s core operations over multiple years. These differences impact how each asset type is managed, valued, and reported in financial statements. Plant assets, also known as fixed assets, are tangible assets that are used in the production process or to generate revenue for a company over a prolonged period of time. These assets are expected to provide economic benefits to the company beyond the current accounting period.
What is a Plant Asset? Definition and Real-World Examples

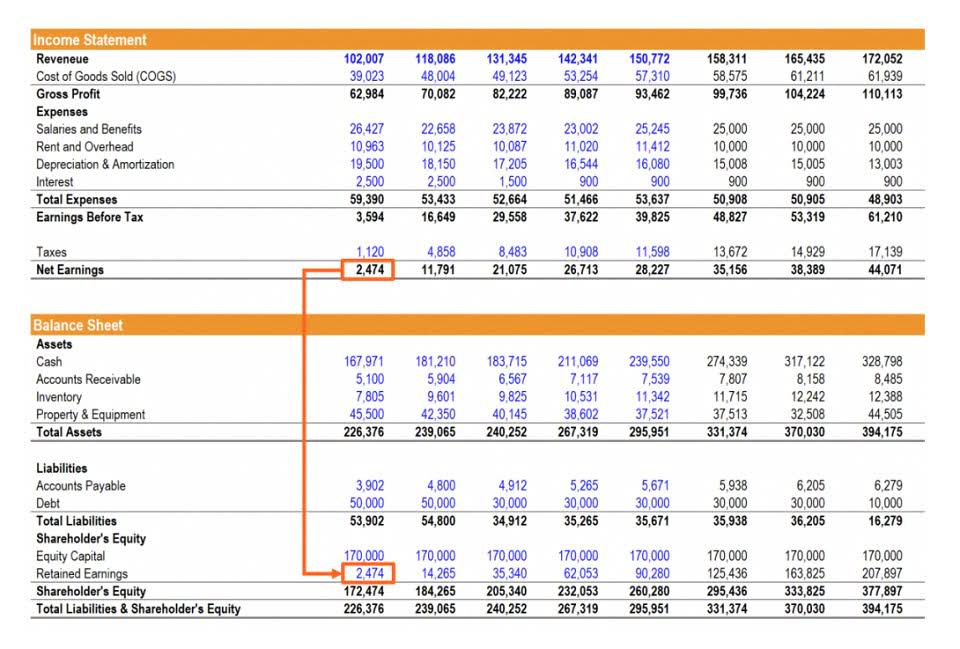
Depreciation on buildings is calculated based on their expected useful life, which can vary depending on construction quality and maintenance. The PP&E account is remeasured every reporting period, and, after accounting for historical cost and depreciation, is defined as book value. To calculate PP&E, add the gross property, plant, and equipment, listed on the balance sheet, to capital expenditures. Companies commonly list their net PP&E on their balance sheet when reporting financial results. Accumulated depreciation helps track the total amount of depreciation taken on an asset fixed assets since its acquisition, indicating how much value has been consumed.

Most Important Financial Statements
- Depending on the industry, plant assets may make up either a very substantial percentage of total assets, or they may make up only a small part.
- Compared to Exxon’s total assets of over $354 billion for the period, PP&E made up the vast majority of total assets.
- Differentiating plant assets from current assets on the balance sheet offers stakeholders a clearer understanding of a company’s operational strength and financial health.
- Companies must consider factors such as the quality, cost, and reliability of the assets, as well as their compatibility with existing systems or infrastructure.
- Each industry tailors its asset management to meet operational needs, balancing the cost, maintenance, and efficiency of these assets to stay competitive and maintain service standards.
- The acquisition cost of a plant asset includes not just the purchase price but also any additional expenses necessary to make the asset ready for use.
To be classified under the category of this kind of asset, it should plant assets be of tangible nature, which means that it should have the feature of being seen or touched. The next plant assets characteristics is that it should be able to provide benefit to the business for more than one year. Effective acquisition of plant assets requires careful planning, thorough research, and attention to detail.
Examples Of Depreciation
In this article, we will talk about non-current tangible assets and, specifically the plant assets. The article will be all about plant assets, their recognition, depreciation, and differentiation from other asset classes. The non-current assets are the company’s long-term assets that last for many years and deliver economic Bookstime benefit. There is a further classification of tangible and intangible non-current assets. The assets can be further categorized as tangible, intangible, current, and non-current assets.
Proper management of the disposal of plant assets ensures transparency in financial reporting and helps maintain accurate records of a company’s asset inventory. It also allows businesses to optimize their asset utilization, free up resources, and make informed decisions regarding replacement or upgrade of assets. The IAS 16 of the IFRS governs the rules regarding recognizing and recording the plant assets in the company’s financial statements. Instead, a part of the cost is periodically charged to the expense account to depreciation the plant assets. What these assets all have in common, that also differentiates them from current assets, is that they are not going to turn into cash any time soon and their connection to revenue is indirect.

Accounting rules also require that the plant assets be reviewed for possible impairment losses. Plant assets represent the asset class that belongs to the non-current, tangible assets. These assets are used for operating the business functions and generating revenues in the financial periods. It is important for businesses to properly identify and classify their plant assets to ensure accurate financial reporting and effective management of these assets.